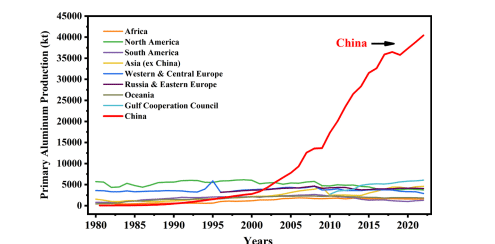
Since the 1980s, the aluminum industry in China has made the most significant progress in two aspects. One is the annual output of primary aluminum that has continuously risen from roughly 400,000 tons in 1983 to 40.21 million tons in 2022, accounting for 58.8% of the total annual global output. Another aspect is the average total energy intensity (i.e. the average comprehensive AC power per tonne of aluminum), which has consistently decreased from 17,560 kWh/t-Al in 1983 to 13448kWh/t-Al in 2022, a reduction of 4112kWh/t-Al over the past 40 years.
Chinalco Zhengzhou Non-ferrous Metal Research Centre has published a new report on how the development and deployment of energy-saving, carbon-reducing, and digital-intelligent technologies in China’s aluminium electrolysis industry plays an essential role in demonstrating and promoting the technological and industrial development of the worldwide aluminium industry.